Reverse Osmosis Membrane vs. Ultrafiltration Membrane: Comprehensive Comparison & Recommendations
1. Introduction
In the field of water treatment, Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Ultrafiltration (UF) are two commonly used membrane separation technologies. Both have distinct advantages in treating water quality, but also significant differences. This article provides a detailed comparison of reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration characteristics, and recommends suitable water treatment systems, such as the DuPont Ultrafiltration Membrane Module (Dupont Ultrafiltration Membrane Module) and Reverse Osmosis Water Treatment Systems (BWRO Reverse Osmosis System, SWRO Seawater Reverse Osmosis System).
2. Comparison of Reverse Osmosis and Ultrafiltration
| Feature | Reverse Osmosis (RO) | Ultrafiltration (UF) |
|---|
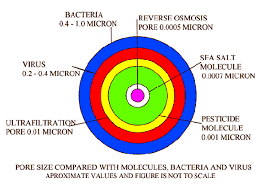
| Pore Size | 0.0001 microns (smaller pore size) | 0.01 microns (larger pore size) |
| Pollutant Removal | Effectively removes chemical pollutants, heavy metals, pesticides, etc. | Removes large particles, bacteria, colloids, proteins, etc. |
| Water Quality | Provides high-quality pure water, removes 99% of dissolved solids | Produces lower quality water, removes particles but not dissolved solids |
| Energy Requirements | Requires pumps and electricity, higher power consumption | No electricity required, low pressure operation |
| Applications | Suitable for drinking water, wastewater treatment, seawater desalination, etc. | Primarily used for washing, can be used for ultrapure water with high-quality tap water |
| Maintenance | Complex structure, higher failure rates, more maintenance required | Simple structure, low maintenance, fewer failure risks |

3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Reverse Osmosis Water Treatment Systems
Advantages:
High-Quality Water: Effectively removes harmful substances like heavy metals, pesticides, chlorine, etc.
Good Taste: Produces water that is pure and free from unpleasant tastes.
Reduces Water Hardness: Effectively reduces water hardness, preventing scale buildup in appliances.
Disadvantages:
High Energy Consumption: Requires pumps and electricity, with potential electrical safety concerns.
Complex Structure: Multiple joints in the system, leading to potential leaks or faults.
Higher Cost: Due to the complexity of the system, it is relatively expensive.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Ultrafiltration Membranes
Advantages:
No Electricity Required: Ultrafiltration systems don’t need electricity and operate under low pressure, offering high energy efficiency.
Simple Structure: The system is simple and has low maintenance requirements, leading to lower operational costs.
Low Cost: Ultrafiltration systems are economically priced and easy to operate.
Disadvantages:
Ineffective Against Chemical Pollutants: Cannot remove dissolved solids, heavy metals, pesticides, or other chemical pollutants in water.
Lower Water Quality: The treated water may not taste as good due to its limited ability to purify.
Does Not Reduce Water Hardness: Cannot address high water hardness issues, which may cause scale buildup in appliances.
5. Differences Between Ultrafiltration Membrane, Nanofiltration, and Reverse Osmosis
| Technology | Ultrafiltration (UF) | Nanofiltration (NF) | Reverse Osmosis (RO) |
|---|
| Pore Size | 0.01 microns | 1-10 nanometers | 0.0001 microns |
| Salt Removal | No salt removal | Salt removal rate >90% | Salt removal rate >99% |
| Common Applications | Household and industrial water treatment, food and beverage industry | Industrial water treatment, some seawater desalination | Seawater desalination, pure water production, industrial water treatment |
| Energy Requirements | Low (no electricity) | Low (low-pressure operation) | High (requires pumps and electricity) |
Ultrafiltration (UF):
Main Advantage: Simple operation, low cost, widely used in home water treatment, food and beverage industries, and wastewater treatment. However, it does not effectively remove dissolved solids, so it is unsuitable for producing drinking water.
Nanofiltration (NF):
Reverse Osmosis (RO):
Main Advantage: RO is the most effective technology for removing dissolved solids, salts, heavy metals, and other pollutants. It is ideal for seawater desalination, drinking water production, and producing high-purity water for industrial use. It requires higher energy consumption and maintenance but produces the purest water.
6. Recommended Reverse Osmosis and Ultrafiltration Systems
If you are looking for suitable water treatment systems for different needs, here are our recommended devices:
DuPont Ultrafiltration Membrane Module: This efficient ultrafiltration membrane module is ideal for industrial and household water treatment, removing large particles, bacteria, and colloids but unable to remove dissolved solids. It is highly suitable for applications requiring high flow rates and low energy consumption.
BWRO Reverse Osmosis System (Brackish Water): A reverse osmosis system designed for brackish water, suitable for seawater desalination, groundwater, and brackish water treatment. It effectively removes dissolved salts, heavy metals, and other harmful contaminants.
SWRO Seawater Reverse Osmosis System: This system is specifically designed for seawater and high-salinity water, widely used for seawater desalination, providing efficient water purification for both industrial and domestic use.
7. Conclusion
Choose Reverse Osmosis: If you need high-purity drinking water or require seawater desalination and industrial-grade pure water, reverse osmosis is the best choice. It effectively removes dissolved solids and pollutants.
Choose Ultrafiltration: If you are focused on low energy consumption, low cost, and simple operation, and if the water quality requirements are not very high, ultrafiltration is a great option for removing large particles and microbial contamination.
By understanding the differences between these two technologies and the recommended equipment, you can make an informed decision and select the most suitable water treatment solution.